Het archief bekijken van donderdag 1 mei 2025
Dagelijks bulletin over zonne- en geomagnetische activiteit van het SIDC
Datum verslag: 2025 May 01 1231 UTC
SIDC Prognose
Zonnevlammen
C-class flares expected, (probability >=50%)
Geomagnetisme
Minor storm expected (A>=30 or K=5)
Proton Flux monitor
Quiet
| 10cm flux | Ap | |
|---|---|---|
| 01 May 2025 | 148 | 025 |
| 02 May 2025 | 148 | 032 |
| 03 May 2025 | 148 | 007 |
Zonnevlekkengebieden en zonnevlammen
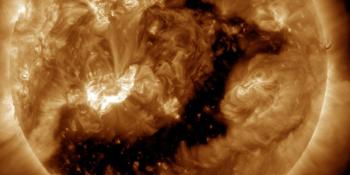
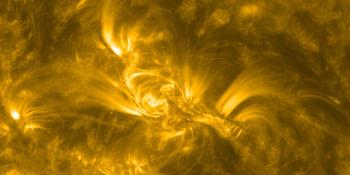
Solar flaring activity was low over the past 24 hours, with only C-class flares detected. The total number of sunspot groups has also decreased, with only five currently visible on the solar disk. SIDC Sunspot Group 476 (NOAA Active Region 4065) has now rotated over the western limb, while SIDC Sunspot Groups 480 (NOAA 4068) and 485 (NOAA 4077) have shown signs of decay. The most active region is SIDC Sunspot Group 469 (NOAA Active Region 4079), currently located at N09E52. This region has a Beta magnetic configuration, showed signs of growth over the past 24 hours, and produced the largest flare of the period: a C2.5 flare (SIDC Flare 4255), which peaked on May 1 at 07:19 UTC. The remaining sunspot groups did not produce any flaring activity. Solar flaring activity is expected to remain low over the next 24 hours, with C-class flares very likely and only a small chance of M-class flares.
Coronale massa uitstoten
No Earth directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs) were observed in the available coronagraph imagery over the past 24 hours.
Coronale gaten
SIDC Coronal Hole 99, a mid-latitude coronal hole with negative polarity, first reached the central meridian on April 29 and is now positioned on the western side of the Sun. The associated high-speed solar wind stream is currently arriving at Earth. Two small coronal holes reached the central meridian today, May 1: SIDC Coronal Hole 109, an equatorial coronal hole with negative polarity, and SIDC Coronal Hole 110, a high-latitude coronal hole also with negative polarity.
Zonnewind
The Earth remains under the influence of a slow solar wind, with speeds ranging between 400 and 490 km/s. The total interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) showed some enhancement and fluctuated throughout the period, reaching values up to 11.7 nT. The southward component of the IMF (Bz) was mainly positive on April 30, then turned negative on May 1, reaching a minimum of -9.8 nT. Around 01:00 UTC on May 1, the phi angle switched from positive to negative polarity. This transition is likely an early indicator of the arrival of the high-speed stream originating from the trans-equatorial coronal hole with negative polarity, the SIDC Coronal Hole 99, which crossed the central meridian on April 29. Solar wind speed is expected to increase later today and into tomorrow. The Earth is likely to come under the influence of this high-speed stream over the next few days.
Geomagnetisme
Geomagnetic conditions were quiet to unsettled until early May 1, around 00:00 UTC, when they reached active levels, with Kp-NOAA and K_BEL both peaking at 4. This increase in activity was driven by an enhanced interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) and the southward turning of its Bz component, which reached a minimum of -9.8 nT and remained negative for the extended period. With the expected arrival of a high-speed solar wind stream associated with SIDC Coronal Hole 99 (a large, elongated trans- equatorial coronal hole with negative polarity that crossed the central meridian on April 29), the geomagnetic conditions may intensify further. Minor storm to storm levels are possible later today and tomorrow, before gradually returning to unsettled conditions, with occasional active periods expected until the influence of the high-speed stream subsides.
Proton flux niveaus
No enhancement or solar energetic particle event has been detected. The greater-than-10 MeV proton flux remained at low levels over the past 24 hours and is expected to stay below the event threshold in the next 24 hours.
Elektronenfluxen in geostationaire baan
The greater-than-2 MeV electron flux measured by GOES 18 and GOES 19 remained below the threshold level over the past 24 hours. The flux is expected to remain below the threshold over the next 24 hours. The 24-hour electron fluence remained at normal levels and is anticipated to stay stable.
Het geschatte internationale zonnevlekkengetal (ISN) van vandaag: 070, gebaseerd op 19 stations.Zon indexen voor 30 Apr 2025
| Wolfgetal Catania | 113 |
| 10cm zonneflux | 148 |
| AK Chambon La Forêt | 019 |
| AK Wingst | 012 |
| Geschatte Ap | 012 |
| Geschat internationaal zonnevlekkengetal | 088 - Gebaseerd op 47 stations |
Overzicht opvallende gebeurtenissen
| Dag | Start | Max | Einde | Locatie | Sterkte | OP | 10cm | Catania/NOAA | Soorten radio-uitbarstingen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geen | ||||||||||
Aangeboden door het Solar Influences Data Analysis Center© - SIDC - Verwerkt door SpaceWeatherLive
Alle tijden in UTC
<< Keer terug naar de dagelijkse overview pagina
Laatste nieuws
Laatste forumberichten
Steun Poollicht.be!
Veel mensen komen naar Poollicht.be om de zonneactiviteit te volgen of om het poollicht te zien, maar met meer bezoekers komen er hogere kosten bij om de servers online te houden. Als je Poollicht.be leuk vindt en het project wilt steunen, kun je kiezen voor een abonnement op een advertentievrije website of een donatie overwegen. Met jouw hulp kunnen we Poollicht. be online houden!
Ruimteweer feitjes
| Laatste X-klasse uitbarsting | 18/01/2026 | X1.9 |
| Laatste M-klasse uitbarsting | 01/02/2026 | M1.9 |
| Laatste geomagnetische storm | 28/01/2026 | Kp5+ (G1) |
| Zonnevlekkenloze dagen | |
|---|---|
| Laatste zonnevlekkenloze dag | 08/06/2022 |
| Maandelijks gemiddeld zonnevlekkengetal | |
|---|---|
| december 2025 | 124 +32.2 |
| Afgelopen 30 dagen | 119.2 +2.7 |